Dimensional Stability in Rigid Flex
As you can imagine, rigid flex is used in many different electronic products and applications. If you’ve ever opened up a laptop computer or mobile phone, you’ll have seen a rigid-flex printed circuit board in action. The hybrid design of these PCBs offers enhanced mechanical stability reducing the risk of fatigue, cracking or failure in high-shock and vibration environments. Rigid flex can also reduce system weight and package size while providing superior signal integrity and functionality.
The bending capabilities of rigid flex provide significant space savings and weight reduction for your device. Additionally, the narrower circuit traces and the ability to mount components on both sides of the PCB increase component density for smaller, more sophisticated devices. These features are ideal for applications that require high-speed or weak signals to be transmitted safely in critical environments.
However, when you’re designing a rigid-flex, there are some important challenges to consider. One of the most critical is ensuring your design has enough mechanical stability. To do this, you’ll need to use the right rigid flex materials and design an optimal layer stack-up.
Another challenge is ensuring your rigid-flex design has adequate flexibility. This can be done by utilizing a variety of flexible materials, including flexible polyimide ribbon, which is used to connect the rigid and flex layers. Using a ribbon can help to prevent signal interference from between the different layers in your rigid-flex design.
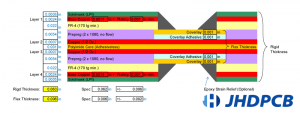
How to Ensure Dimensional Stability in Rigid Flex
Lastly, you’ll need to ensure your rigid-flex design meets mechanical requirements and will be manufacturable. You can do this by establishing and maintaining a symmetry and balance in both copper distribution and dielectric materials. In addition, you’ll want to make sure your rigid-flex layers are positioned in the center of your layer stack. This will allow you to avoid low-pressure areas during manufacturing that can cause imaging, etching and plating problems.
A well-designed rigid-flex PCB is essential for meeting your product’s engineering and production goals. To do this, you’ll need the right tools that will provide a complete view of your design and enable you to prepare it for manufacturing. Altium Designer provides a single, integrated platform that integrates all of these essential rigid-flex design tools. Watch the webinar to learn more about how you can design a rigid-flex PCB successfully with Altium Designer.
Rigid-flex is often found in electronic devices that have a unique shape or need to fold, flex or bend. These include wearable electronics such as fitness trackers and health monitors, conformal heating elements in aerospace systems, medical devices, and a variety of other uses. To ensure that your rigid-flex is ready for manufacture, check out this guide to avoiding the most common DFM mistakes in rigid-flex design. By following these simple steps, you can be sure that your rigid-flex is designed for dimensional stability, flexibility, and signal integrity. With a little bit of planning, you’ll be able to get your rigid-flex from concept to manufacturing in no time.